Spray hemp extract Liposomes
Vaping, oral sprays, skin cream, liposomes? If you’re new to the world of hemp, the variety of ways to take just one plant’s extract may be a little confusing. What method of dosage is best? Also, what do terms such as “liposome” even mean? If you have noticed liposomal sprays in Elixinol’s product range and are interested in trying hemp extract liposomes, it’s worth knowing what you’re getting, and why they are made that way.
Quite simply, the reason why hemp extracts are sometimes sold as liposomal sprays is because of their potential to improve absorption. This may also possibly bypass any destructive effects that stomach acid or other digestive secretions may have.

So why do liposomes boost absorption?
The answer lies in what liposomes actually are: tiny spheres made from cholesterol and naturally-occurring phospholipids1. A phospholipid is a fat with a phosphate attached to one end2. The phosphate allows it to mix with “water-based” substances and environments, while the fat can interact with “oil-based” substances. Water-based, or water-soluble, substances have molecules with ends that are more charged – one positive, one negative – like a battery. In contrast, oil-based (fat-soluble) substances have little to no charge on the ends. Water-soluble substances can only mix with each other, and so can fat-soluble substances; this is why oil and water do not mix but fat and oily substances readily combine.
Liposomes may solve the oil/water solubility challenge for cellular absorption of
When nutrients and beneficial phytochemicals of plants enter the body, they are affected by this principle. While the insides of the stomach, intestines and blood vessels are watery areas, the cell membranes which nutrients and phytochemicals must pass through to enter the bloodstream, are made of fat.
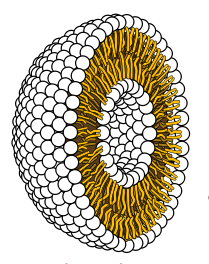
A Liposome, with the phosphate heads (white) facing outwards, and the fatty acids (yellow) inward.
This means that many nutrients such as vitamin C which can only mix in water, must combine with specific transporters on the membranes of the cells which line the small intestine. However, those nutrients that mix with fat or oil-based substances often get chaperoned by fatty acids (the breakdown products of fats) to the intestinal cells. They then join up with other fats & fat-soluble nutrients on leaving these cells in order to enter the blood. This is the specific benefit of liposomes. Like these fatty acids, cell membranes are also made of phospholipids and cholesterol, which protect cells’ contents and allows nutrients and other cell contents to move through the watery outer world.
Liposomes may improve drug delivery for pharmaceutical applications
Liposomes are seen as showing promise in the pharmaceutical side of medicine, as they have shown an ability to improve drug delivery without the same level of toxicity as traditional forms of administration. This can work for either water or fat-soluble substances. One study3looking for a way to protect the vitamins C and E in fruit juice found that there was a high rate of encapsulation of both vitamins.
Improving CBD delivery
As CBD is non-soluble in water, liposomes could improve its transmission through the body. One situation where they could improve CBD absorption is in topical use4. A study on mice showed that liposomal CBD resulted in a “significant accumulation” of the cannabinoid in the skin and underlying muscle. This CBD was also able to prevent inflammation. This was an important discovery, as CBD is poorly absorbed through the upper layers of skin on its own. As CBD is also often poorly absorbed orally, liposomal delivery (orally OR through the skin), may be a superior alternative. It is clear that more human trials would help expand our understanding of liposomal delivery for CBD
References
1: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23432972
2: Tortora, GJ & Derrickson, B, 2012, Principles of Anatomy & Physiology, 13th edn, Wiley
3: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0963996911004650
4: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365903004152
Would you like to know more about the world of medical cannabis and CBD? Do not hesitate to contact us.
Write an e-mail at info@hempoilshop.gr or leave a message to social media channels, Facebook @ hempoilshop.gr or Instagram!
www.hempoilshop.gr 211 4010715