Is your endocannabinoid system in balance?
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
Let’s give a brief review regarding the endocannabinoid system. It is a group of specialized lipids with receptors that produce and degrade the enzymes. Endocannabinoids are known to regulate and affect several physiological functions, like appetite, pain, inflammation, thermoregulation, intraocular pressure, sensation, muscle control, energy balance, metabolism, sleep health, stress responses, motivation/reward, mood, and memory.
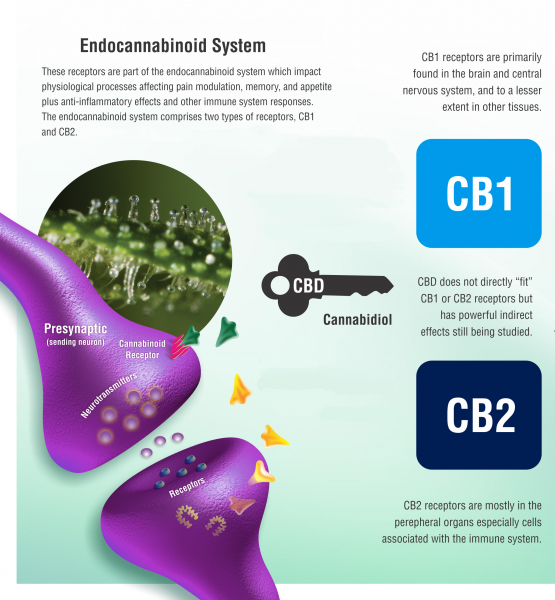
What are the Cannabinoid Receptors?
The Cannabinoid Receptors are a significant set of cell membrane receptors mostly known with the serpentine shape. It looks like a lock and key system, where the receptors are similar to «locks», and the ligands compounds bound with them are resembling «keys». They have approximately seven sections that pass through the outer cell membrane. The cannabinoid receptors are also bound, with G proteins, where a lot of signaling magic happens as a molecule or a compound binds to the outer section of the receptors. The three main ligands bound with the cannabinoid receptors are lipophilic (fatty or lipophilic compounds) included the endocannabinoids (produced within the body), the phytocannabinoids (derived from the plants, such as cannabis), and the synthetic cannabinoids (created in the labs copying the natural cannabinoids). The cannabinoid receptors are divided into two main subtypes of receptors, known as CB1 and CB2. They may seem to have similarities but they mostly differ depending on the tissue or the organ system within the body. CB1 receptors are found mostly in the brain but are also detected in the lungs, kidneys, liver, fat, heart, muscles, and bones. CB1 receptors are mostly associated with the psychoactive and euphoric aspects of THC. However, CB2 receptors are detected mainly in the immune system and blood cells, but also, even with less density,in the nervous system, liver, guts, muscles, and bones.
How do cannabinoid receptors contribute to the Endocannabinoid System balance?
Endocannabinoid tone/balance is the correlative activity of CB1 vs. CB2, at any given moment. A lot of studies show that CB1 dominance is associated with increased perception of stress, anxiety, increased appetite, decreased nausea/vomiting, and pain while boosting immune surveillance, which is linked with certain cancer types. On the contrary, CB2 dominance is mostly related to decreased inflammation and tissue injuries, combined with progress in metabolic health, insulin signaling/sensitivity, satiety, and energy balance.
Based on this information, several scientists are concentrating on specific CB1 blockers that could improve many of the symptoms of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a set of health risk factors leading to heart disease, stroke, diabetes. It includes factors like high blood pressure, excess body fat around the waist, and irregular cholesterol levels. There are already studies demonstrating the peripheral inhibition of CB1 reduces blood pressure and blood sugar, balances the cholesterol levels leading to fat loss, lowers the risk for cardiovascular disease and diabetes Type II. Some research in this area has already demonstrated that peripheral CB1 inhibition reduces blood pressure and blood sugar and improves cholesterol levels, as well as leads to visceral fat loss resulting in a lower risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
What does a balanced endocannabinoid system look like?
Recent biochemical and behavioral data show that the best possible activation of CB1 receptors stimulates neurochemical changes similar to the anti-depressants and behavioral effects compatible with the antidepressant/antistress potency in mice. These findings enhance the endocannabinoid system importance, which is known for the proliferation, distinction, survival, immunodeficiency of the often-neglected organ system ( skin cells, and hair). Several skin disorders (psoriasis, eczema, acne, dermatitis, systemic sclerosis, etc) which lead to undesirable skin cell growth and inflammation, can be soothed by targeting and manipulating the endocannabinoid system.
Summary
“The endocannabinoids are the basic modulators of the synaptic function. Activating the cannabinoid receptors, present in the central nervous system, they regulate various central functions acting as lipid messengers. As experimental tools advance, the endocannabinoid system-induced effects and their main mechanism expands. Retrospective signaling is the main way in which the endocannabinoids mediate short-term or long-term plasticity shape in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses. However, a lot of data underline that the endocannabinoids may signal in a non-retrospective way. The endocannabinoid system is also subject to plastic changes except for the expressed synaptic plasticity. The synaptic cannabinoid signaling is mechanically more complex and different than originally thought. In this review, we focus on the endocannabinoid signal progress while we highlight their role as effective regulators of synaptic function in the mammalian brain.”
Need help? Would you like to learn more about medical cannabis and CBD? Do not hesitate to contact us at info@hempoilshop.gr, or reach us at our social media channels.